News attention
12
2020
-
02
Scientific Research News | Research Progress of novel coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19) (XII)
1. 2019-nCoV Epidemic Alert
■ On February 2, at the press conference of the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, Chen Xuefeng, deputy director of the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, put forward four suggestions on how to deal with a series of psychological stress reactions brought about by the epidemic: First, to stabilize the mood, if there are no typical symptoms such as fever and dry cough, there are no confirmed or suspected patients around, and rarely go out, the possibility of being infected is very small, do not panic and anxiety excessively. The second is to analyze rationally, carefully observe your physical condition, judge whether the uncomfortable symptoms and the typical symptoms of the new crown pneumonia are consistent, if it is more consistent, or go to the fever clinic in time, if not, it may be other physical problems, if necessary, you should also go to the hospital, under the guidance of the doctor. The third is to change behavior, if you know that you are healthy, but you still can't control your worry, then try to divert attention, find a thing to put yourself into doing for a long time, and change the psychology of excessive fear through these ways. It should be reminded that there are very few people who have such a situation, he firmly believes that he is infected with new crown pneumonia, and even goes to the hospital for repeated treatment, even if doctors and medical examinations believe that he is not infected, he firmly believes that he is infected. If so, we still recommend that we and our families take this problem seriously, and it is best to go to the psychology department and psychiatric department of the hospital in time to seek professional help to avoid long-term emotional tension leading to irrational behavior and harming ourselves and others. Fourth, take the initiative to seek psychological assistance. In order to reduce and prevent psychological distress caused by the epidemic and prevent the occurrence of extreme events, the National Health Commission has supported the establishment of psychological assistance hotlines in various localities to respond to the epidemic on the basis of the original psychological assistance hotlines. If you can't alleviate the adverse stress response on your own, you should call the hotline in time and seek professional help.
■ Regarding how to ensure the supply of daily necessities for residents in closed communities, Chen Yueliang, director of the Department of Grassroots Power Building and Community Governance of the Ministry of Civil Affairs, said: "At present, various localities have mainly taken the following measures: First, standardize the management of community access. Under the condition of strict protection and temperature measurement, try to allow each family to send personnel to go out to purchase daily necessities to meet the needs of normal life. The second is to arrange community workers to purchase on behalf of others. Provide support and care for special groups, families in difficulty, and people in home isolation, help buy all kinds of daily necessities, and deliver them to their doorsteps. The third is to organize the distribution of goods around the community. Connect with some large chain enterprises and supermarkets and convenience stores around the community, and set up daily necessities sales points within the community. The fourth is to set up community express delivery and takeaway delivery areas. In order to facilitate community residents to purchase daily necessities online, some communities have set up express delivery and takeaway delivery areas, where couriers deliver daily necessities purchased by residents to designated areas and receive them contactlessly by recipients. Reduce the gathering of people while ensuring the normal delivery of express takeaway. Some communities that have the conditions to disinfect courier personnel and vehicles and goods are allowed to put the courier into the smart express box after completing the registration and disinfection procedures. ”
■ The research team from Shanghai Life Science Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences published a review paper "Global Coronavirus Research Situation Analysis and Its Enlightenment" in the journal "Chinese Clinical Medicine", which analyzes the current status and trend of global coronavirus research based on bibliometrics, citation analysis and knowledge graph, sorts out the knowledge context of coronavirus-related research, and provides reference for the prevention and control of coronavirus-induced diseases at present and in the future. The paper pointed out that in the past 20 years, the global coronavirus research has been significantly improved, and the results have been remarkable, which has played an important supporting role in the prevention and control of related infectious diseases and epidemic prevention and control. Despite this, human understanding of coronaviruses and the diseases they cause is still limited, there are many unknowns and gaps, and there are still many unknowns and gaps that need to be further improved, and the NCP (novel coronavirus pneumonia) epidemic is a typical example. Fortunately, scientists around the world, especially Chinese scientists, responded quickly, quickly isolated and identified pathogens in a short period of time, and proposed effective prevention and control measures, and follow-up research on 2019-nCoV virus traceability, transmission mechanism, virus detection, disease diagnosis and treatment, drug and vaccine research and development and epidemic assessment are also being carried out [1].
■ On February 2, according to the Guangdong Provincial Drug Administration, the dialysis anti-pestilence granules (formerly known as "Pneumonia No. 8 Square") (traditional Chinese medicine preparation) declared by the Eighth People's Hospital of Guangzhou have been approved for clinical use in the province's designated hospitals for the treatment of new coronary pneumonia. "Pneumonia No. 1 Fang" is the clinical experience of Tan Xinghua, chief physician of the Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangzhou Eighth People's Hospital, and the clinical application of "Pneumonia No. 1 Fang" to treat 1 confirmed patients with pneumonia (mild disease) infected by the new coronavirus, after 50 week of clinical observation, all patients' body temperature returned to normal, and none of the patients turned severe. At present, the prescription is limited to patients with mild confirmed and suspected cases, which can improve the clinical symptoms of novel coronavirus pneumonia (mild disease) and has a tendency to reduce the occurrence of severe pneumonia, but it cannot be used as a preventive formula.
2. 2019-nCoV Biology Research Progress
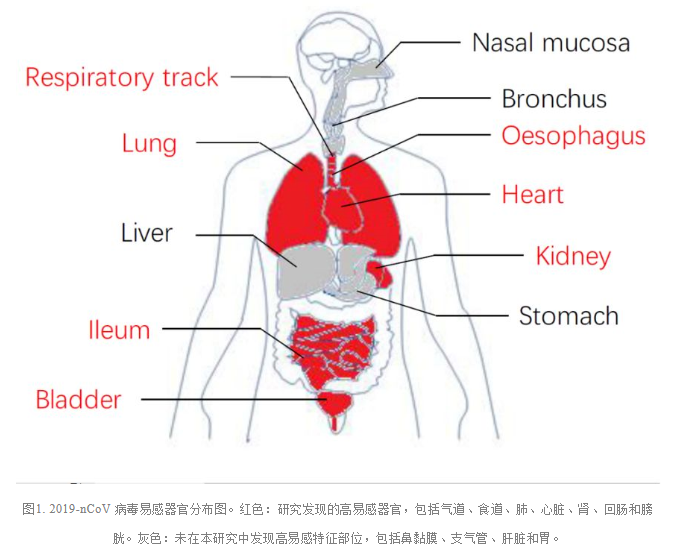
■ On February 2, Professor Han Zeguang's team from the Institute of Systems Biomedical Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, published a research paper in Frontiers of Medicine, an academic journal published in China. The study takes the conclusion that the 8-nCoV coronavirus invades cells through human ACE2019 receptors as a breakthrough, in addition to taking alveolar type II (AT2) cells as the primary target for the invasion of this coronavirus due to high ACE2 expression, speculating that the virus may also attack other organs of the human body through ACE2. Therefore, the latest single-cell RNA sequencing data was used to analyze the expression of ACE2 in organs and cell types related to the main physiological systems of the human body, including the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and urinary systems, and then constructed a risk distribution map of human organs vulnerable to the invasion of the 2-nCoV coronavirus. The results showed that the heart, esophagus, kidney, bladder and ileum all had similar or higher ACE2019 expression than in the alveoli, suggesting that these organs may be attacked by the novel coronavirus. AT2 cells, cardiomyocytes, renal proximal tubular cells, and ileum, esophageal and bladder epithelial cells contained in these organs may become portals for viral invasion due to high expression of ACE2. The results showed that in addition to lung cells, there are other organs such as the heart, kidneys, small intestine, etc. that are at risk of virus invasion. Although the virus often first infects the lungs through the respiratory tract, as the disease progresses, especially viremia, the virus may infect more internal organs through the circulatory system, which may be related to later symptoms such as renal failure and myocarditis [2].
3. 2019-nCoV epidemiological study
■ Zeng Dajun and others from the School of Artificial Intelligence of the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Shenzhen Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science (Longhua) and other institutions pointed out through the analysis of population flow before Wuhan's lockdown: before January 1, the infection coefficient R23 was 0.3. This data is comparable to the R24 (0-2) of SARS, higher than that of influenza (5-2) and Ebola virus (3.1-5.2). This explains its highly contagious nature and hints at the need for measures such as lockdowns [5].
■ Dr. Min Kang of the Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and others analyzed the travel history of confirmed cases in Guangdong Province and divided the cases into two categories: infection in other places and infection by locals. They analyzed data from 1 cases in Guangdong Province as of January 27, with the average age of confirmed patients being 188.48 years old, with 8.49% (5/93) male, of which 188% (75/141) had a travel history to Wuhan and 188% (9/17) had a non-Wuhan travel history to Hubei. In addition, by sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of viral nucleic acids infected in the same family, it was proved to be the same subtype. These evidence suggests that at that time, Guangdong Province was dominated by imported cases, but local human-to-human transmission had already occurred [188].
Bibliography:
1. Chen Daming, Zhao Xiaoqin, Miao Yougang, et al. Analysis of the Global Coronavirus Research Situation and Its Enlightenment [J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020, 27 (1): 1-12
2. Xin Zou KC, Jiawei Zou, Peiyi Han, Jie Hao, Zeguang Han. The single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to Wuhan 2019-nCoV infection. Front Med.
3. Cao Z, Zhang Q, Lu X, et al. Incorporating Human Movement Data to Improve Epidemiological Estimates for 2019-nCoV. medRxiv 2020:2020.02.07.20021071.
4. Kang M, Wu J, Ma W, et al. Evidence and characteristics of human-to-human transmission of 2019-nCoV. medRxiv 2020:2020.02.03.20019141.
Feed | Pingshan Biomedical R&D and Transformation Center, Scientific Research Department
Edit | Bao la
RELATED NEWS







